Brick walls are probably the most common building elements in
construction of a house in India. These walls form basic units for
creating rooms that make up a house. The walls besides being space
dividers are also structural elements that transfer the load of the roof
to the ground. Brick walls are constructed on strip spread or raft
foundations that support the walls. The walls are constructed using
bricks and mortar. These can also be constructed with various structural
qualities and thicknesses.
Brickwork
Brick walls are constructed by joining bricks
with cement mortar in arrangements called English Bond, Flemish Bond or
Rat Trap Bond. These bonds give different external appearances to the
wall. All construction systems of brick walls are such devised that
vertical cross joints in any layers are staggered. The bricks thus
bonded form a solid mass that does not split when the wall is loaded
with live loads and dead loads.
Classification of Brick Work
The classification of brick work according to the quality of brick is following.
- First class brick work
- Second class brick work
- Third class brick work
First Class Brick Work
First class brick
work is made by using first class bricks and cement mortar. This brick
work is used for load bearing walls. It is made in rich mortar in which
the cement and sand ratio is from 1:3 to 1: 6.
First class bricks are identified by their uniform color and a
ringing sound when struck. The bricks are equal in size and have even
edges and surfaces. These bricks do not chip and don’t have any cracks.
First class bricks do not absorb water more than 1/6 of their weight.
There is no salty residue when the bricks are dry. First class bricks
have a minimum crushing strength of 105.kg. Per sq. cm

Bricks of first class quality
Second Class Brick Work
Second
class bricks work is made by using second class bricks and cement
mortar. These bricks also have the property of first class bricks but
are not very regular or even in shape. These bricks should not be used
for load bearing walls for more than two storey buildings. Second class
bricks have minimum crushing strength 70.kg per sq. meter.

Second class quality of bricks
Third Class Brick Work
This type
of brick work is made by using third class bricks and cement mortar or
mud mortar. Third class brick work is not made in any Govt. work.
Generally this type of brick work is made for temporary work in private
sector.
Mortar
Mortar is a mix used to bind brick, stone etc to each other.
It
can thus be seen as a binding material that bonds bricks, stones to
make a wall or for cladding purpose. Normally cement mortar is used in
brickwork in present day construction though lime mortar can also be
used but it requires superior craftsmanship and is hence infrequently
used.
Cement Mortar
Cement mortar is a
mix of cement and sand with water. The cement is binding material which
requires sand as a filler material. This cement mortar mix in wet state
is plastic and binds two materials when it dries. Mortar is generally
defined as 1:2 or 1:3 or 1:7 etc. This means that one part of cement is
mixed with 2, 3 or 7 parts of sand.
Precaution for mixing cement mortar
The following steps should be taken carefully while mixing materials for cement mortar.
- The mix should be made on a dry, clean, flat surface.
- The mix should be as per specifications.
- The mix should be by volume.
- The quantity of water should be such that the mix can be easily
spread over bricks or applied on a vertical surface. Water more then
required quantity may spoil the mix and it can reduce the strength of
masonry.
- The mix should be used within half an hour of its preparation.
Brick Wall Foundations
Brick wall foundations are normally made as strip foundations.
These
are continuous along the length of wall and hence called as strip
foundations. These form structural components of construction system by
which the load of whole building is transferred to the ground.
Foundations
are made in dug out trenches so that a hard stable surface on which the
building is supported can be obtained because the top surface of the
ground normally does not have load bearing capacity to take the load of
the building. The other reason is that foundations can by this method be
hidden from view. The architect needs to provide a foundation plan that
indicates exactly where the foundation trenches are to be dug.
The foundation trenches are dug after being marked on center line
principle on the site according to architect’s drawings. The size of
trench varies with the thickness of walls and the load bearing capacity
of the soil. The base of dug trench is rammed to solidify the surface.
On rammed surface a layer of cement concrete is laid. This is normally 6
to 8 inches thick. This base concrete layer needs to be cured for it
attains its expected strength. Base concrete layers or courses of bricks
are laid to create a stepped base that would help in distributing the
load over a larger surface of the foundation.
Precautions during construction of brick wall foundations
- The marking of foundations must be absolutely accurate as the location of walls depends on these markings.
- The trenches should not be dug in rainy season. The bricks, mortar mix and cement concrete mix should be as per specifications.
- The width and depth of the trenches depends on loading and soil
conditions. As the foundation is an expanded base to distribute the load
coming on it over a large area on ground. The width of the wall
foundation depends on whether the wall is a load bearing wall, a non
load bearing wall, a partition wall or a toe wall.
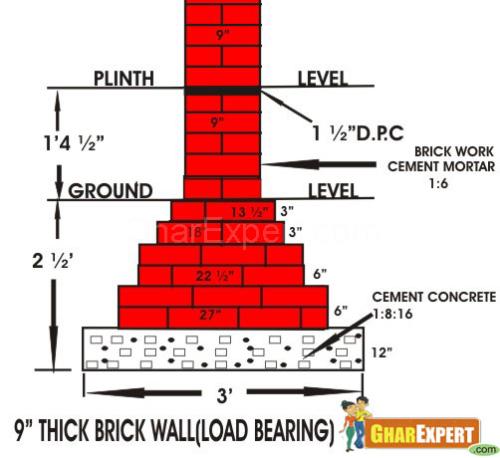
Load Bearing Walls
The walls that support beams and roof slabs.
- These walls take the load of super structure and transmit it to the ground through foundation.
- These can also serve the purpose of dividing the space into required rooms etc.
- These are also accommodating door and windows where required.
- These are of 9” or more thickness.
- Such walls are made in first class bricks and rich mortar.
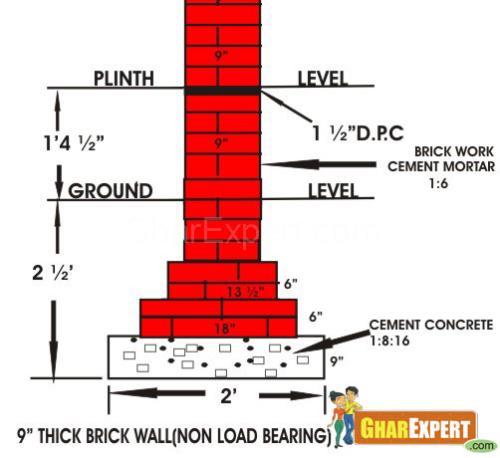
Non Load Bearing Walls
- These walls serve the purpose of dividing the space into required rooms etc.
- These are also accommodating door and windows where required.
- These can be made into thin sections to save the space.
- Non load bearing walls are only partition having no load of super
structure so these can be easily changed whenever required to change the
space of the room.
- These walls are made 3 inches, 4.5 inches and 9 inches thick as per the requirement of the site.
Super Structure:
The word super structure used in construction work means/denotes following.
- Brick work from DPC level to the roof level/slab level.
- If columns provided in drawings then RCC columns to be laid.
- Rain water pipe is to be embedded in walls.
- Fixing doors, windows and ventilators frames in walls.
- RCC (Reinforced Beam & slab for roof) including M S Steel bars according to the designs.
- Tile terracing lay with brick tiles on the top of the roof slab.
- Fixing doors and windows shutters.
- Fixing cupboard in the rooms and Kitchen etc.
- Fixing iron grills for safety of the house.
- Providing cement plaster on ceiling and walls.
- Laying floors including base coat.
;