Roof Flashing

Roof flashing technique is used to prevent water leakage from the roof. It is a sheet made of metal and which requires installation at roof valleys/ gutter, chimneys, skylights, ridges, roof-wall intersections of the roof. The roof flashing is usually made from rust resistant metals like galvanized steel, aluminum or copper. It may be fabricated from plastics, roofing felts, or rubber etc.
Galvanized sheet metal roof flashing is widely used roof flashing whereas Aluminium and Copper roof flashings are used where cost of maintenance matters. Copper is the most durable but it is costly and has advantages over the other metals as the corners of copper can be soldered to make the joints water tight. This article tells you about roof flashing locations, roof leaks testing, roof flashing materials, and types of roof flashing.
How to test roof leakage for roof flashing?
Roof leakage testing is a way to find the place and cause of leak in the roof of your house. Wait for dry weather and ask one person to go onto the roof with a garden hose while the other person to go inside the attic with a bucket and strong light. The person on roof floods the roof with water while the other person watches carefully until the leak appears into the roof. Once the leak is found, drive a nail into the hole to mark the location of leak.
Where to apply roof flashing on roof?
Roof flashing is fixed at roof top edge, pipes, chimney, and edges resting on the wall, skylights, and valleys / gutter and at the joints of top roofing sheets/slates to fasten them against water penetration or leakage. The roof flashing protects building from water leakage and dampness and ensures the safety of materials and contents of the building against water leaks.
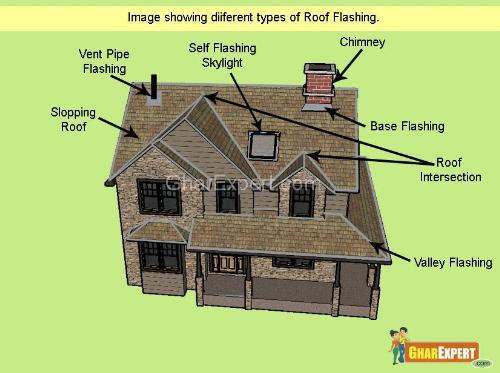
Roof Flashing Types
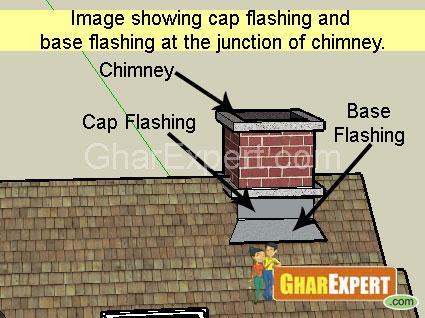
Chimney Flashing
Chimney flashing is installed around the base of chimney to protect house from leakage. This flashing is fixed where walls of chimney rest on roof shingles. It has been categorized in two parts i.e. Cap flashing and Base flashing.Cap flashing is provided at projection or with walls at the point of intersection of walls and roof shingles. To avoid leakage of water, 15 cm to 20 cm cap flashing is overlapped on Base flashing. A groove is provided in wall or parapet to fix Cap flashing. To avoid wind pressure and strengthen the edge of flashing, the edge of Cap flashing metal sheet is bent from 12 mm to 25 mm.
Cap flashing is installed on the slope of the roof. Along the slope of roof Cap flashings are arranged in steps where upper steps overlap the lower steps at least by 15 cm to avoid any leakage. Base flashing should be inserted in such a way on the roof consisting of slate, tiles or asphalt shingles as the joints are water tight living no possibility of leakage.
To avoid differential movements caused by change in weather, fix Cap flashing and Base flashing independently. If the flashings are improperly fixed or installed carelessly, they may be damaged by ice or storm. If both flashing are bent up to each other at the joint, they will not move properly according to weather changes. To avoid leakage the joints should move freely but care should be taken that these joints are tight.
Continuous Flashing
This flashing is applied to protect the joints of vertical wall and sloped roof. The rain water from the slope of the roof drains out from the building but some quantity of water leaks through the joints of roof and wall creating leakage. To avoid the leakage at the edge of vertical wall and roof, continuous flashing is used.Drip Edges Flashing
This flashing prevents water seepage along the edges of rakes and eaves. Drip edge flashing is used under roofing felt adjacent to eaves and over roofing felt adjacent to rakes.Skylight Flashing
The joints around skylights are covered with skylight flashing at the base and step flashing on the sides to avoid leakage.Step Flashing
Stepped flashing is used where a sloped roof meets a masonry wall. To prevent leakage from the sides of walls, skylights, chimney, step flashing is used. These flashings are installed at right angle, connected the roof tops and walls of the structure. The vertical edge of flashings is usually embedded into the wall so that the water can’t leak behind it.Valley Flashing
Valley flashing is provided at the joints where the two roofs meet to protect roof from leakage. The channel/gutter is provided on the supports to drain out rain water from the roof.Vent Pipe Flashing
Vent pipe flashing is fixed over chimneys and pipes. It comes in the shape of cone with a flange at the base and works into the shingles when the roofing is applied.Roof Flashing Materials
Roof flashing should be tough, rust-proof, weather proof, low in maintenance and accommodate weather changes. Roof flashings are fabricated from metals like Aluminum, Copper, Galvanized Steel, Lead coated Copper, Stainless Steel, and Zinc which are rust proof, tough. The flashing is also available in plastic, rubber, roofing felt etc. The following are some roof flashing materials.1. Galvanized Steel Roof Flashing
You can make this roof flashing by coating steel sheet with a layer of zinc alloys. Use galvanized nails while fixing galvanized steel flashing as fasteners of different metal will corrode soon. The flashing should be bent mechanically for good results.Advantages of Galvanized steel roof flashing
- Economical material
- Gives a better look
- Less fabrication and installation cost
- Available in long pieces that can be fixed quickly
Disadvantages of Galvanized steel roof flashing
- Rust and decay in short time if used without paint
- Bad effect in polluted and acidic environment
- Not molded into any shape easily
- Needs heating for molding to the required shape which spoils galvanizing
2. Stainless Steel Roof Flashing
Stainless steel is durable flashing material specially suited for tough and corrosive environments. It is good to fix on valleys and counters. It is formed as per site requirement as it is not available in preformed shape. Stainless steel nails should be used while fixing these flashings.Advantages of stainless Steel roof flashing
- Most durable
- Can be turned into any shape
- Not affected by ecological corrosion like acid rain or salt spray
- Not spoiled if fixed in direct contact with masonry or concrete surface.
Disadvantages of stainless Steel roof flashing
- Costly
- High labor for fabrication and installation
- Difficult to shape in the field being stiff and rigid material
3. Copper OR Lead Coated Copper Roof Flashing
Copper is one of most durable and rust proof material. It requires technique to cut, design, fabricate and install. This flashing also needs skilled and experienced craftsman for proper installation.Advantages of Lead coated Copper roof flashing
- Long life
- Weather proof
- Low maintenance cost
Disadvantages of Lead coated Copper roof flashing
- Costly material
- Expensive fabrication and installation
4. Aluminum Roof Flashing
This roof flashing is durable and versatile and can be fixed around chimney, vent etc. It is available in various thicknesses. You can increase the life of this roof flashing by painting or anodizing. Aluminum can be turned into any shape easily according to requirement. Thick aluminum flashing has no reaction in salty and corrosive environment. The fastener of any other material may be harmful to aluminum roof flashing which is easy to install.Advantages of Aluminum roof flashing
- Economical in comparison to copper
- Inexpensive fabrication and installation
- Soft in nature and can easily be molded in any required shape.
Disadvantages of Aluminum roof flashing
- Spoiled in short time if it is used without painting or anodizing
- Handled carefully being soft in nature otherwise leakage may start
5. Rheinzink Roof Flashing
Rheinzink flashing consists of 98% high grade zinc and 1 % copper and 1% titanium alloys. It is available in sheets and has natural blue grey or grey green color. It can be painted.Advantages of Rheinzink roof flashing
- Works easily into complex shapes
- Less expensive than lead-coated copper
Disadvantages of of Rheinzink roof flashing
- Requires ventilation to protect the underside of material from white rust and corrosion which reduce its life
- Needs bituminous material to reduce the influence of alkali, acid etc.
 The following measures should be taken during construction of water tank to prevent the leakage. These preventive meas
The following measures should be taken during construction of water tank to prevent the leakage. These preventive meas
 Flat roof will be a better choice for which they want full use of building space. It appears flat with a slope for getting rid of water pounding. Flat roof can be used as an outdoor area for amusement or recreational purposes.
Flat roof will be a better choice for which they want full use of building space. It appears flat with a slope for getting rid of water pounding. Flat roof can be used as an outdoor area for amusement or recreational purposes.
 A kind of roof makes a vital and lasting statement about your house. The right roof should give you a secure home and also last several years, even a lifetime. Understanding about different roofing shingles can gives you the right choice about your house. Every shingle has its own benefits and drawbacks. Here are a few of the more popular types of roof shingles in the market.
A kind of roof makes a vital and lasting statement about your house. The right roof should give you a secure home and also last several years, even a lifetime. Understanding about different roofing shingles can gives you the right choice about your house. Every shingle has its own benefits and drawbacks. Here are a few of the more popular types of roof shingles in the market.
 Modern Ceiling Design ideas are one of the most beautiful things that can happen to your home design. Here view some pictures of home Ceiling designs.
Modern Ceiling Design ideas are one of the most beautiful things that can happen to your home design. Here view some pictures of home Ceiling designs.
 Are you worried about irritating roof leaks that destroy contents of the building and have adverse effects on the health of inhabitants of the house. This write up tells you about several causes, effects and repairs of roof leaks.
Are you worried about irritating roof leaks that destroy contents of the building and have adverse effects on the health of inhabitants of the house. This write up tells you about several causes, effects and repairs of roof leaks.
 Skylights or roof windows such as dome skylight, tabular skylight, sun tunnel skylight, and pyramid skylight can give you good health and cut on electricity bills since they are rich source of natural air and lighting in modern homes. Let’s know various types, designs and installation methods of skylights.
Skylights or roof windows such as dome skylight, tabular skylight, sun tunnel skylight, and pyramid skylight can give you good health and cut on electricity bills since they are rich source of natural air and lighting in modern homes. Let’s know various types, designs and installation methods of skylights.
 Skylights introduce healthy atmosphere and can save large amounts of energy in homes. They create energetic feel and provide more natural light and fresh air. Read more about skylight ventilation in this article.
Skylights introduce healthy atmosphere and can save large amounts of energy in homes. They create energetic feel and provide more natural light and fresh air. Read more about skylight ventilation in this article.
 Skylights or roof windows not only provide ventilation solution but also enhance the beauty of your home. By installing these skylights you can expand indoor area and convert it into beautiful living area. Here are complete details about skylights or roof windows
Skylights or roof windows not only provide ventilation solution but also enhance the beauty of your home. By installing these skylights you can expand indoor area and convert it into beautiful living area. Here are complete details about skylights or roof windows
 Green roof is the best solution in this era when global warming and pollution are always hot news. Green roofs not only enhance the beauty of one’s home but help us stay close to the nature also. More on green roof is here.
Green roof is the best solution in this era when global warming and pollution are always hot news. Green roofs not only enhance the beauty of one’s home but help us stay close to the nature also. More on green roof is here.
 Steel roofing is tough, stable and easy to install. These words are enough to describe steel roofing. So here are some quick guidelines about installing steel roofing.
Steel roofing is tough, stable and easy to install. These words are enough to describe steel roofing. So here are some quick guidelines about installing steel roofing.
 ACC roofing covers more space with less intermediate supports. In the following article you will come to know advantages, disadvantages and other important information regarding Acc roofing.
ACC roofing covers more space with less intermediate supports. In the following article you will come to know advantages, disadvantages and other important information regarding Acc roofing.
 Iron Sheet roofing has timeless appeal coupled with strength and versatility.
Iron Sheet roofing has timeless appeal coupled with strength and versatility.
 A solid roof on building is very important for everybody living in the house. The roof should be constructed in a way that assures you great safety. Here are given details about different types of roofing.
A solid roof on building is very important for everybody living in the house. The roof should be constructed in a way that assures you great safety. Here are given details about different types of roofing.
 Kota stone flooring is a subtle blend of grandeur and luxury giving the interior and exterior a gorgeous look.......
Kota stone flooring is a subtle blend of grandeur and luxury giving the interior and exterior a gorgeous look.......
 To get maximum ventilation and natural light in your house, make sure the building is properly oriented. Orientation of building saves energy and provides comfortable living as well. This article tells you about various factors and benefits of building orientation.
To get maximum ventilation and natural light in your house, make sure the building is properly oriented. Orientation of building saves energy and provides comfortable living as well. This article tells you about various factors and benefits of building orientation.
 Preview some of the most impressive pictures of kitchen from GharExpert Gallery.
Preview some of the most impressive pictures of kitchen from GharExpert Gallery.
 A solid roof on building is very important for everybody living in the house. The roof should be constructed in a way that assures you great safety. Here are given details about different types of roofing.
A solid roof on building is very important for everybody living in the house. The roof should be constructed in a way that assures you great safety. Here are given details about different types of roofing.
 Frames of doors and windows are most important parts of your doors and windows. They are available in different size, height, width and shapes. Frames hold locks and hinges and support door and windows to shut and open easily. Here is what you need to know about different doors and windows frames.
Frames of doors and windows are most important parts of your doors and windows. They are available in different size, height, width and shapes. Frames hold locks and hinges and support door and windows to shut and open easily. Here is what you need to know about different doors and windows frames.

Roof Flashing

Roof Flashing

Roof Flashing

asphalt shingle roof for gable roof

Flash door designs

Flash door

beautiful slop roof house design

Roof Ceiling

Roof Ceiling and Blinds

Roof Ceiling

Application sketch - roof water proofing

Bathroom Ventilation through roof
Concrete roof slab cutting using core cutting machine
Concrete roof slab cutting work without vibration
concrete roof slab cutting using diamond saw core cutting machine
Concrete roof slab cutting using core cutting machine
concrete roof slab cutting by core cutting machine and lifting by chain block-9841125344

Roofing in East Flanders, Belgium

Bamboo Roofing

Bamboo Roofing

Roof Flashing

Roof Flashing

Roof Flashing

Bathroom Ventilation through roof

Roof Ceiling

Roof Ceiling and Blinds

Roof Ceiling

Application sketch - roof water proofing

Damp Roofing with Adequate Space

Air Space for Flat Roof of Thermal Insulation

False Ceiling Treatment for Flat Roof

False Ceiling Treatment for Pitched Roof

Roof Airport

Shell Roof

Veranda with Curved Roof

Stone Used In roof

Roof

Roof

roof finish

Aluminium Roofing sheet

Roofing sheets

Exterior View with Roofing Shingles

ROOF CEILING

ROOF N FLOOR

Aluminum Shingles Roofing

2d Front elevation of the house with slanted roof

ROOF CEILING

Different Composite Roofing Shingles

Sloped roof house Elevation

Exterior view of Sloped roof home

Copper Roofing

Exterior view of Sloped roof home

Flash door designs

Different ways for Copper Roofing

Wooden Porch Swing

Standing Seam Aluminum Roof

Sloped roof house exterior under construction

Ceiling Design

Porch

Roof Construction

Roof Construction in progress

Roof Steel Design

Modern Elevation design front-house-view with Curved roof

Cool Roof Coat to reduce temperature of top floor

Exterior view of Sloped roof home

Porch

Sloped roof house Elevation

3d design of house exterior with sloped roof